Ground Penetrating Radar
At Fellow Tree LLC we can accurately assess tree decay by utilizing Ground Penetrating Radar technology. This is a quick and non-invasive procedure to analyze in a digital format possible decay or soft spots in the trunk, as well as roots depth and density. This technology has been proved to be extremely useful for a wide range of applications, from planning construction sites by protecting the roots, conducting a Level 3 Risk Assessment and generating baseline data for long-term treatment or monitoring. We offer this service along with a report as part of our assessment process.
History Of Ground Penetrating Radar
GPR (Ground Penetrating Radar) technology was first time put in use in the early 1900’s when Gotthelf Leimbach and Heinrich Löwy designed a system that could use continuous radar waves to locate buried objects. Later on, in 1926 Dr. Hülsenbeck’s research lead to the development of a similar device that used radar pulses instead of continuous waves, leading to the improvement of depth resolution. More significant research only occurred in the 1970’s mostly with military applications. The 1972 Apollo 17 mission carried a GPR unit in orbit around the moon. More commercial applications followed when the first device affordable to the consumer was sold in 1975. Today GPR is used worldwide in a variety of endeavors and academic disciplines such as archeology, forensics, construction, and biomonitoring.
Ground Penetrating Radar Applications in Urban Forestry
- Analyze wood density and predict potential decay
- The GPR scans and software produce a digital display of root layout, density and depth. This can be used during planning and construction to establish TPZ (Tree Protection Zone) to avoid root damage.
- The GPR can be used to scan under a variety of surfaces such as: turf, bare ground, concrete, asphalt, bricks, pavers, and buildings. Thus, any utilities and other hardscape conflicts could be avoided
- TO accurately indicate areas of root loss in declining trees
The GPR does not disturb the trees or the soil and allows multiple measurements to reveal decline or progress in trees growth.
Examples:
- Trunk scans
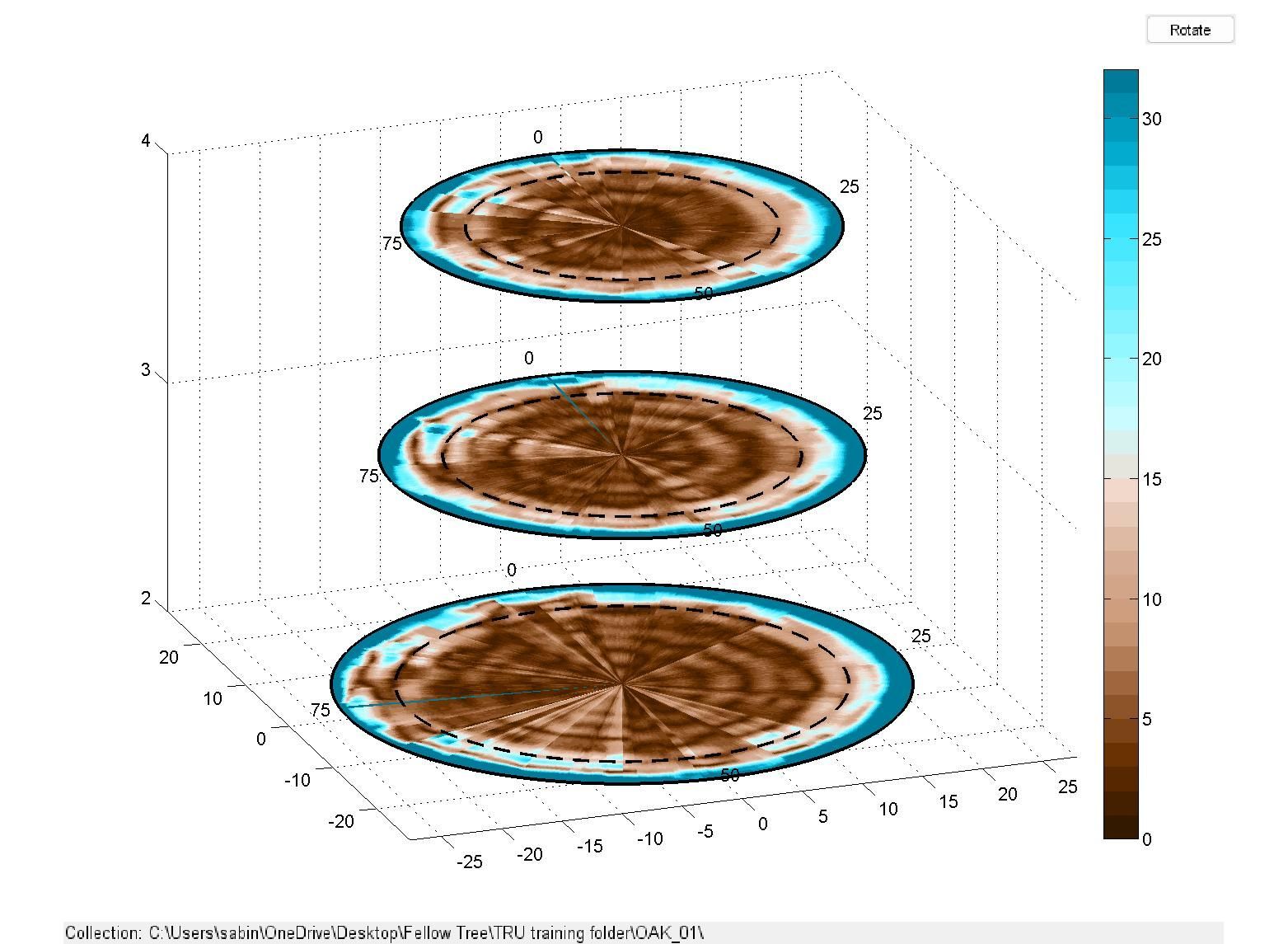
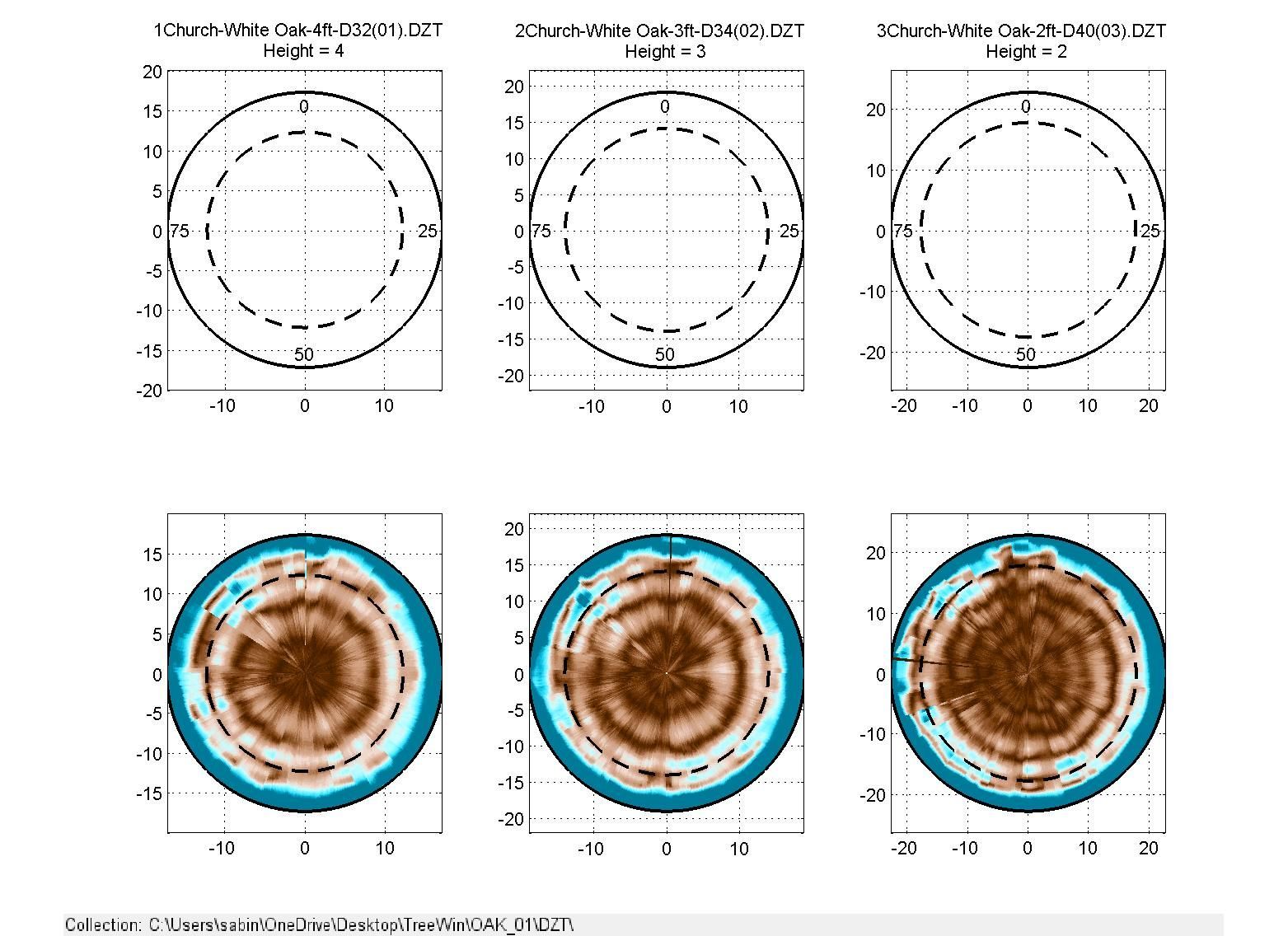
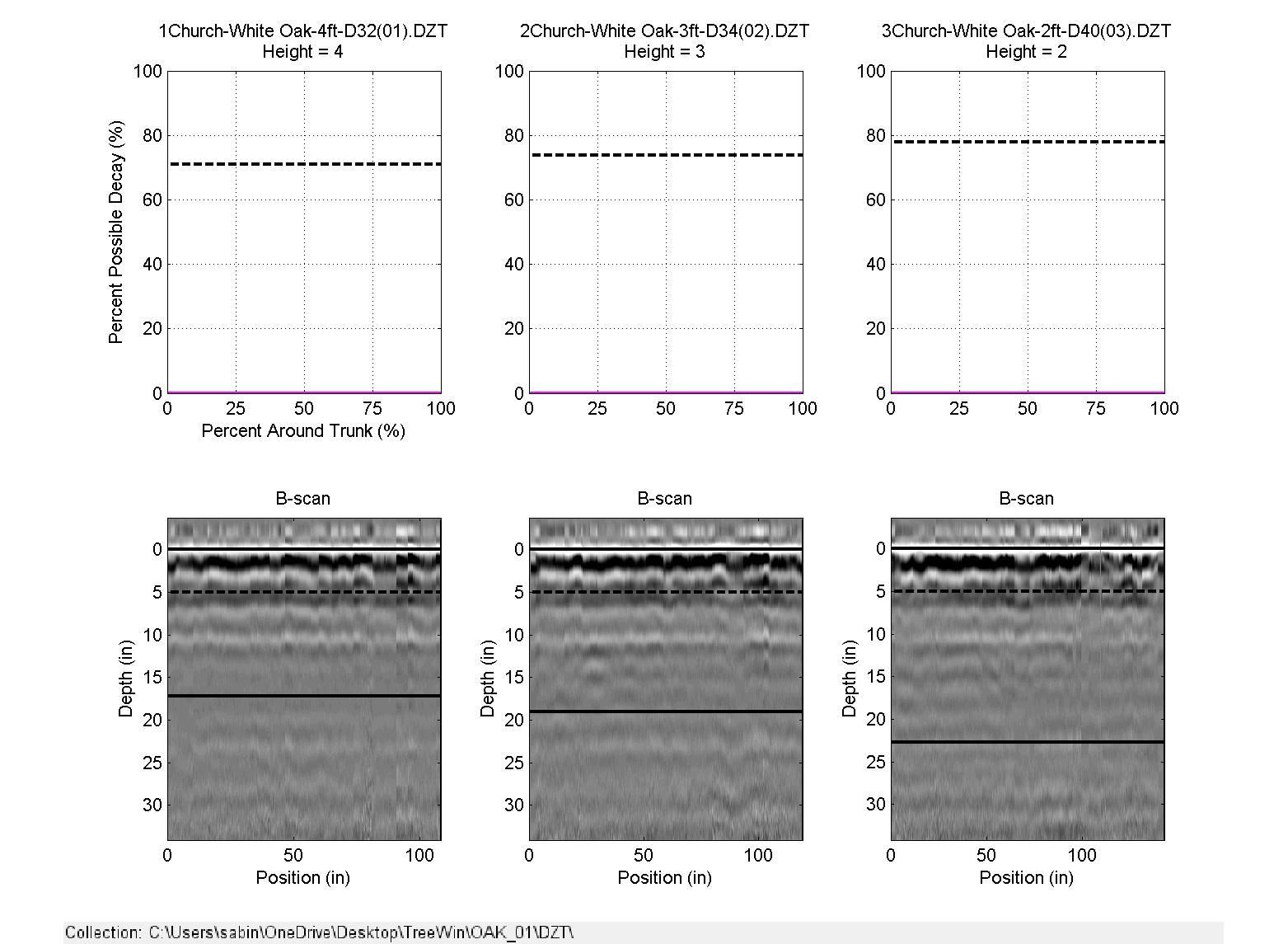
The GPR (Ground Penetrating Radar) uses radio waves to penetrate the wood and provides an image (radargram) of the internal structure of the tree. The TBA processing software is analyzing the radargram to measure different variations and patterns of the signal that might be indicative of low wood density or decay. The magenta areas in the picture are areas of predicted compromised wood.
Trunks with solid stems
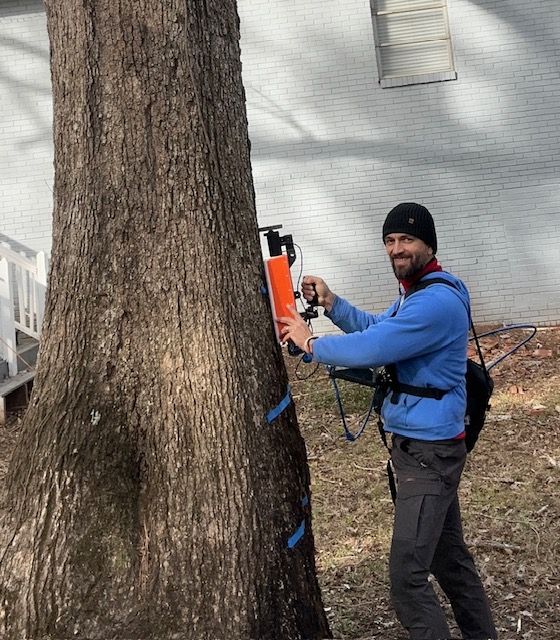
This is the scan of a red oak and the picture of the tree itself. The brown within the doted line indicates solid wood.
The picture of the actual tree
 Button
Button
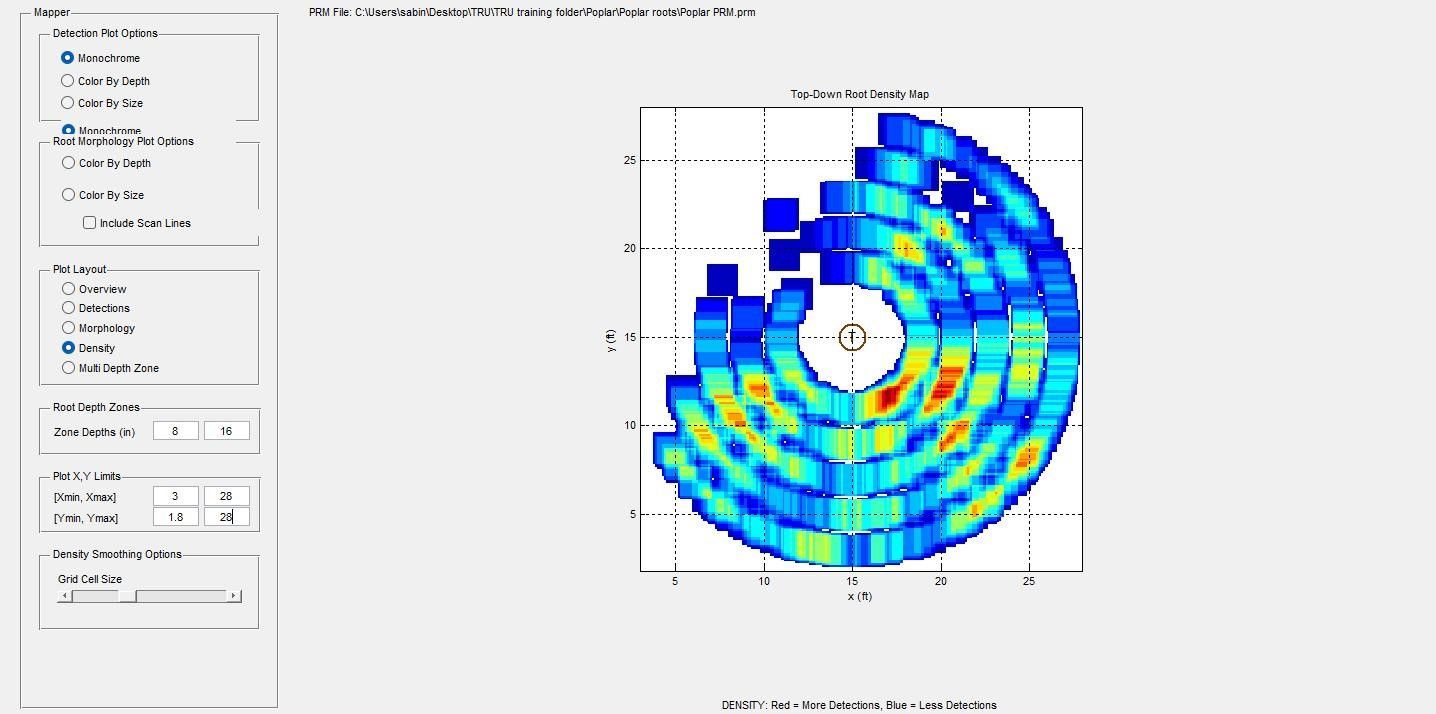
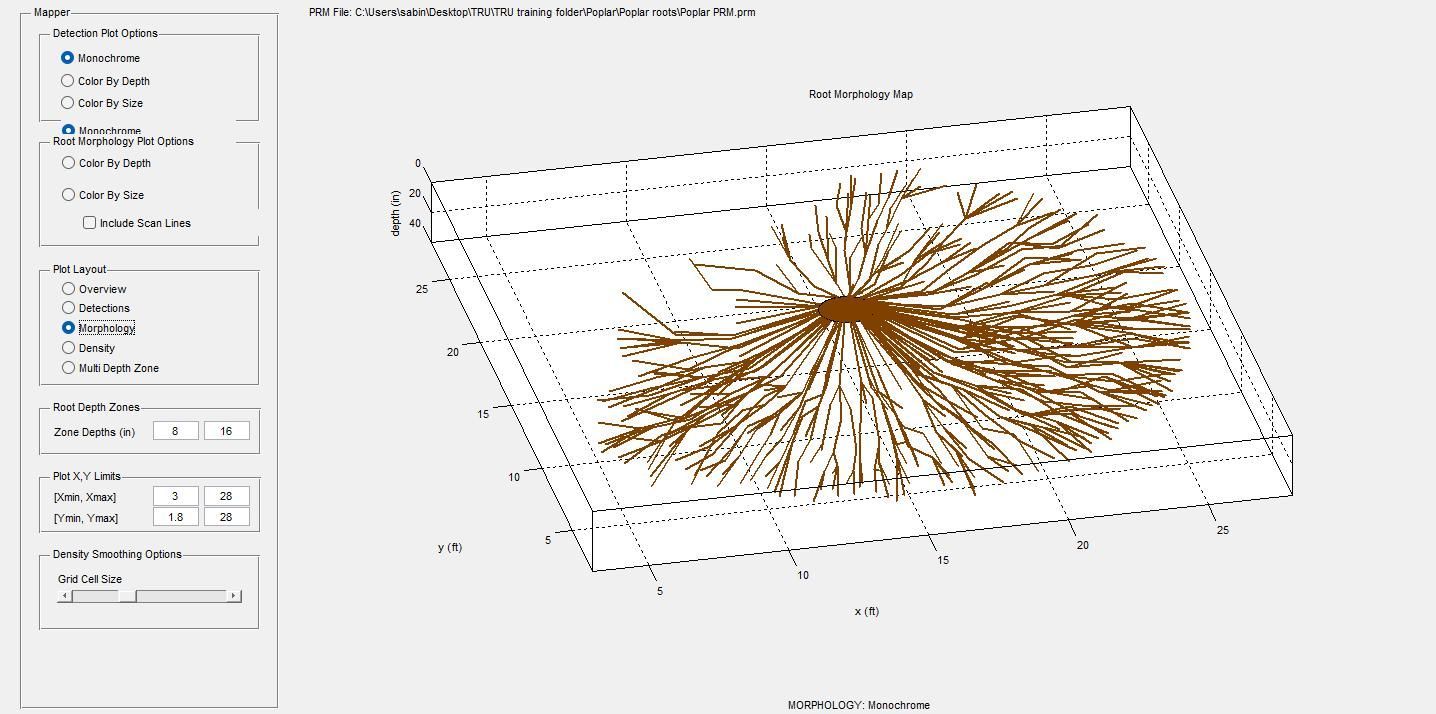
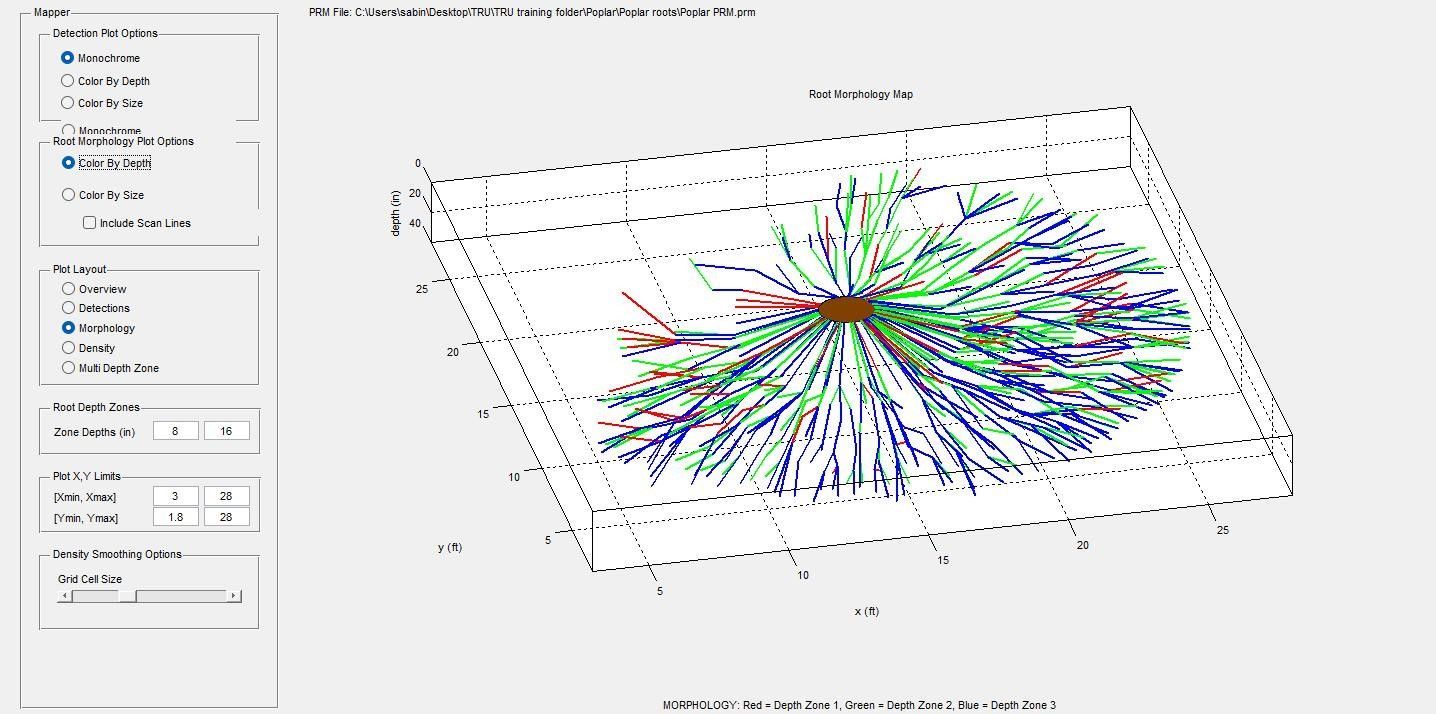
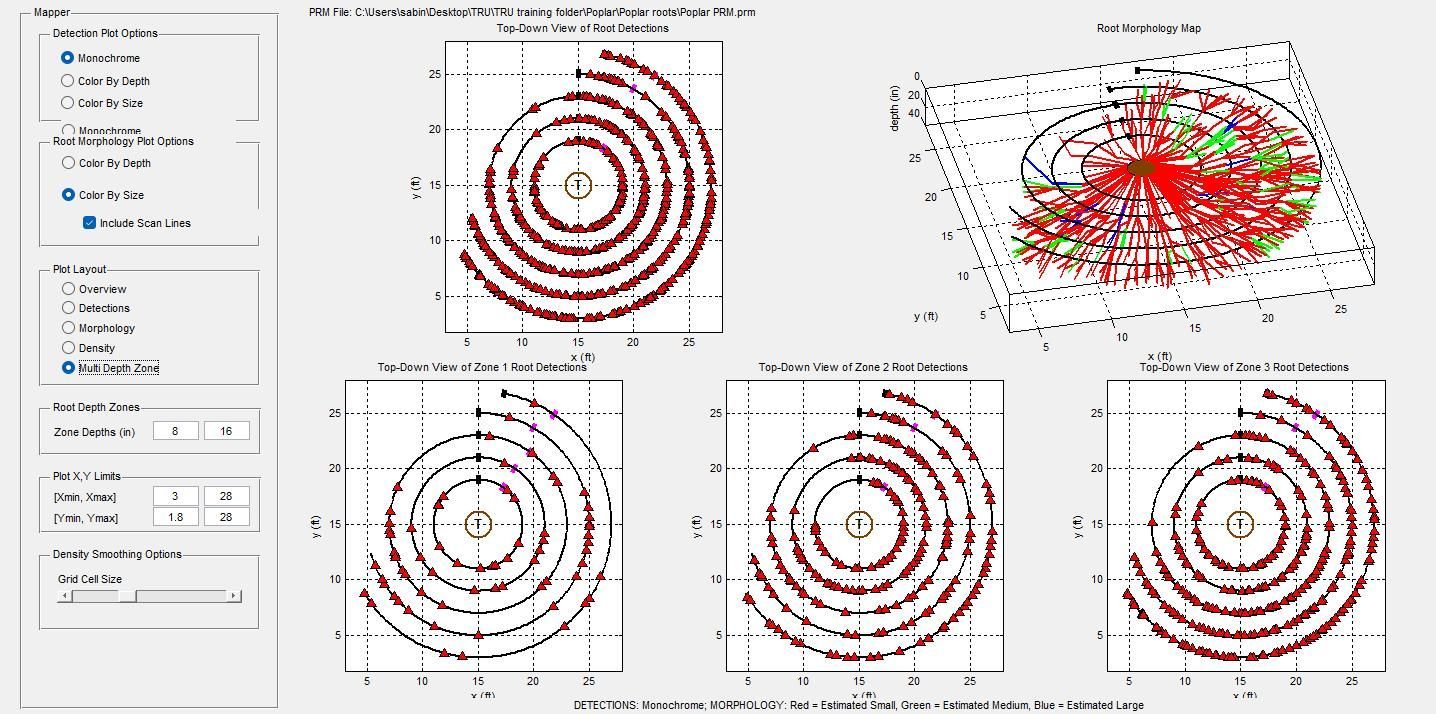
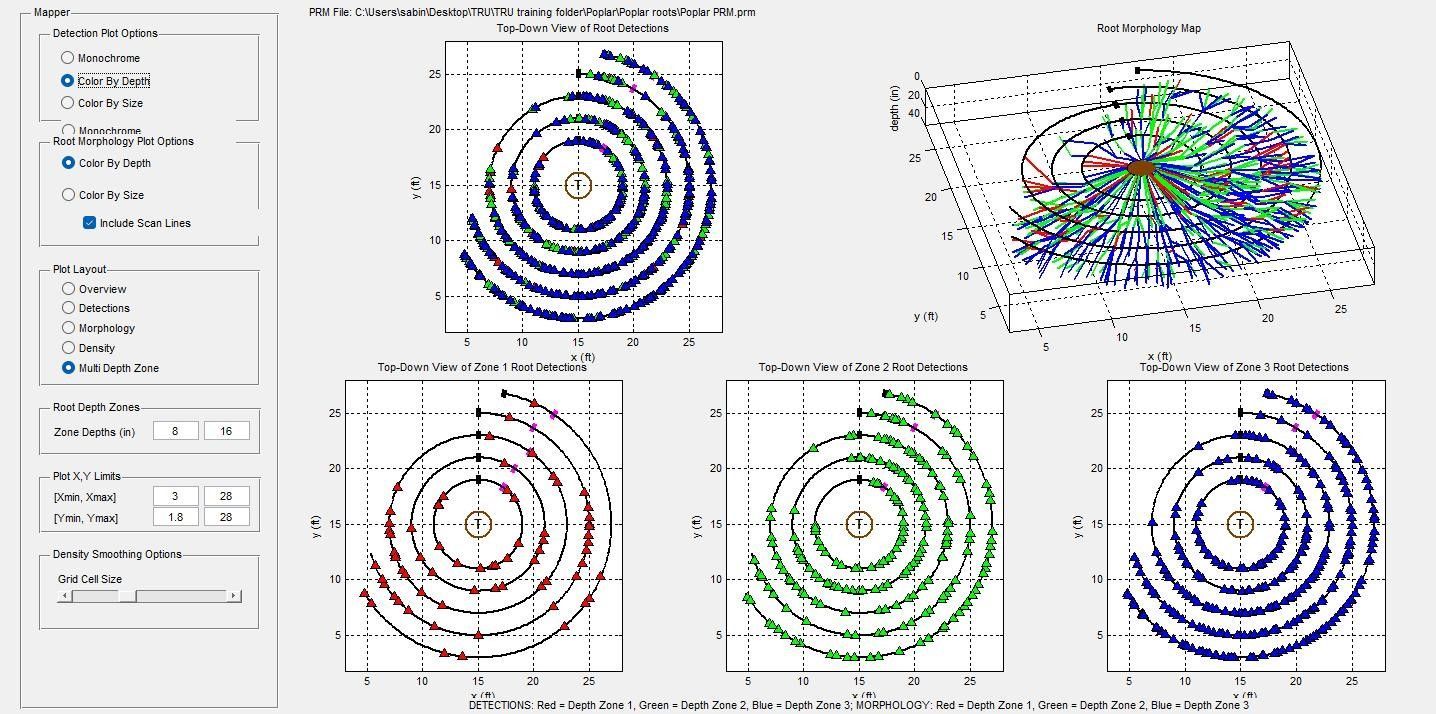
2. Root Scans
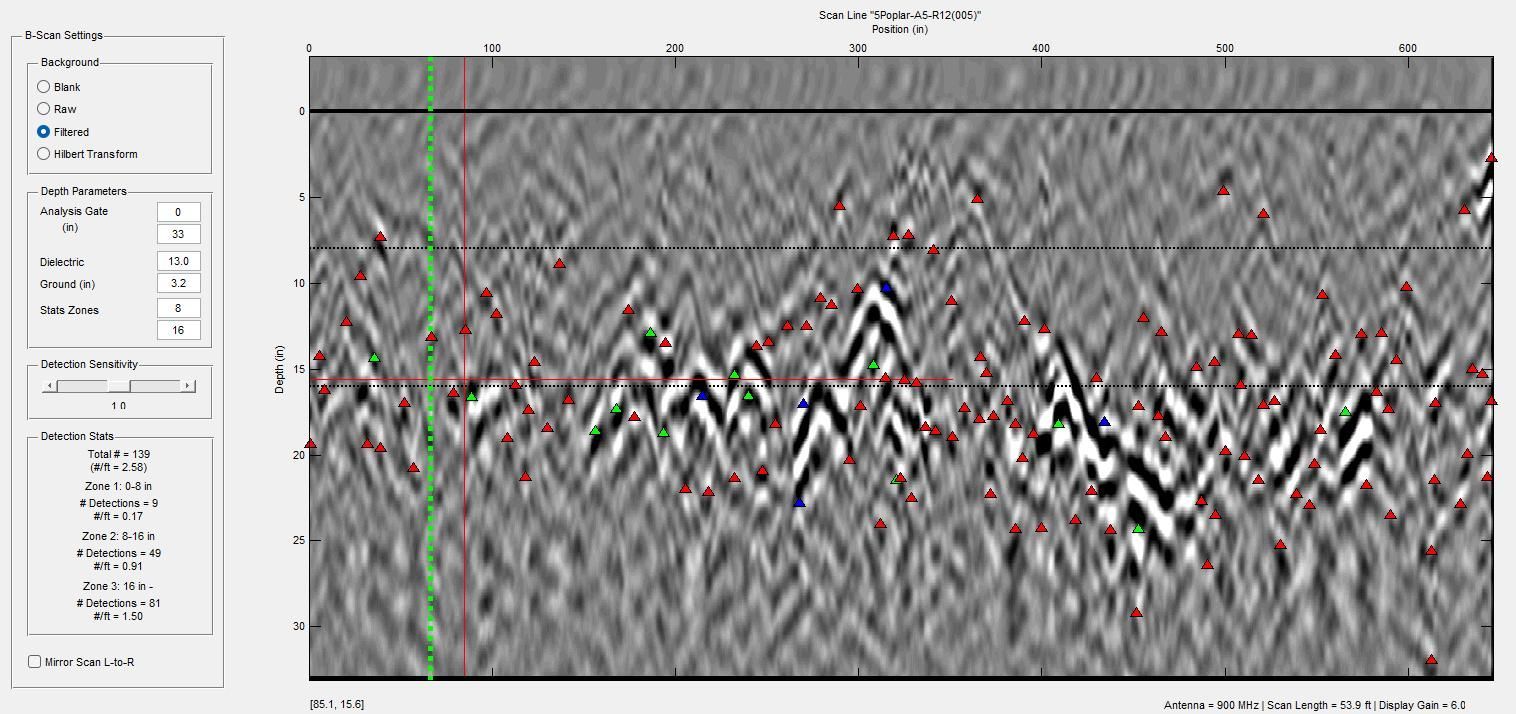
GPR (Ground Penetrating Radar) can penetrate though concrete, asphalt or brick to identify roots lying beneath the surface.
These are the roots of a poplar tree where trenching has been performed on one side of the tree. As a result the roots have been severely compromised.
Follow Us
All Rights Reserved | Fellow Tree
Kennesaw, GA 30152 | (803) 727-4403



